PSGY4009
Experimental design for functional imaging
2025-09-30
1 Today
- Who am I? Who is everyone?
- A quick overview of the module.
- What to expect, assessment/coursework?
- 101 of functional MRI and experiment design.
2 Overview
| Timetable week | Date | Lecture | Lecturer | Lecture |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 02 | 2025-09-30 | 1 | Schluppeck / Griffiths | Overview, fMRI & study design. |
| 03 | 2025-10-07 | 2 | M Schürmann | Basic neuroanatomy |
| 04 | 2025-10-14 | 3 | D Venerio | Brain stimulation & study design. |
| 05 | 2025-10-21 | 4 | W v Heuven | Language |
| 06 | 2025-10-28 | Reading week (no lecture) | ||
| 07 | 2025-11-04 | 5 | D Schluppeck | Q&A, experimental design, coursework |
| 08 | 2025-11-11 | 6 | L Cragg | Developmental neuroimaging. |
| 09 | 2025-11-18 | 7 | B Griffiths | Vision + brain imaging |
| 10 | 2025-11-25 | 8 | J Derrfuss | Cognitive control, attention, and working memory. |
| 11 | 2025-12-02 | 9 | R Filik | Moral Cognition |
| 12 | 2025-12-09 | 10 | M Ashgar / D Schluppeck | Module recap, Touch / Somatosensation (+- decision making) |
3 Assessment
Written assignment (max 3000 words) including a 250 word abstract.
Details on moodle (2024/25).
3.1 What? How?
How can fMRI and/or brain stimulation be used to study different neuroscience questions? Cover at least two topics and/or methods from the course.
4 Today’s lecture
A brief introduction to fMRI.
Scope and limitations of the fMRI method.
Principles of experimental design in psychology.
Experimental design for fMRI.
5 Learning objectives
By the end of the lecture you should be able to:
- Understand what fMRI measures.
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of fMRI.
- Evaluate different experimental designs.
6 LO
fMRI basics
7 fMRI basics
MRI uses static and oscillating electromagnetic fields to detect different biological tissue properties.
functional MRI measures changes in blood oxygenation over time.
BOLD signal: blood oxygen level dependent
8 Example research questions
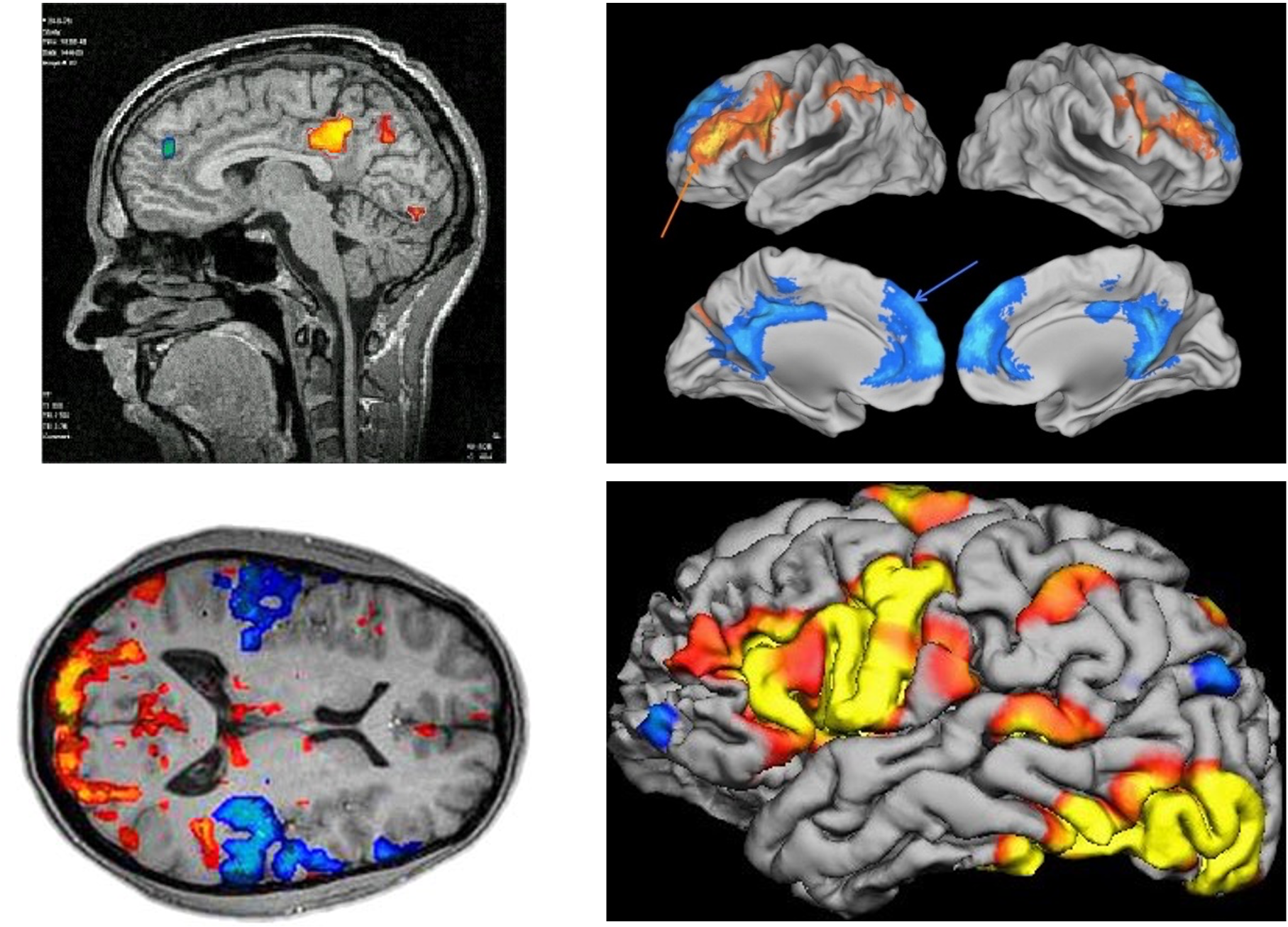
 Where are the areas more active in Condition A than in Condition B?
Where are the areas more active in Condition A than in Condition B?
How do pre-defined regions of interest respond in different experimental conditions?
9 Experimental “pipeline”
Prepare
Theory ➡️ Research Question ➡️ Hypothesis
Plan & do
Experimental Design ➡️ Piloting ➡️ Data collection
Analyse & report
Preprocessing ➡️ Analysis ➡️ Interpretation
10 Study
11 General thoughts (BOLD)
What does the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal measure?
- neuronal activity?!
- populations of neurons (excitatory, inhibitory)
- spikes or (pre-)synaptic activity
12 General thoughts (Signal/Noise)
(fMRI) signals are weak + noisy.
- How does that limit voxel size?
- Short events, minimum durations?
- Need for averaging?
- Blocks versus “event-related” designs?
13 General thoughts (Variability)
Details of brain anatomy vary across individuals.
- What does this mean for group studies?
- Individual subjects results first?
- Data in 3d or 2d (cortical surface?)
14 Example data / images
15 fMRI measures changes over time

16 Example: visual cortex
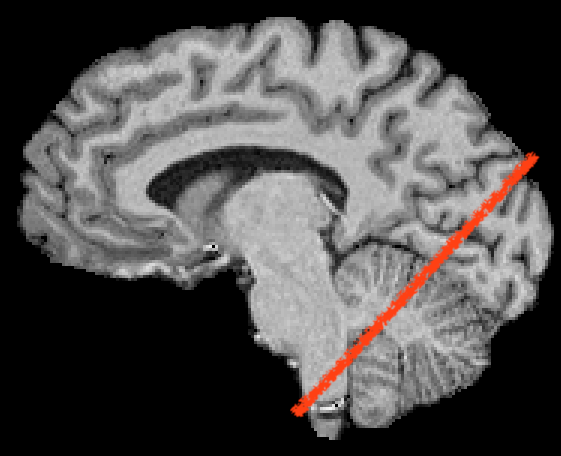
17 Example: visual cortex (movie)
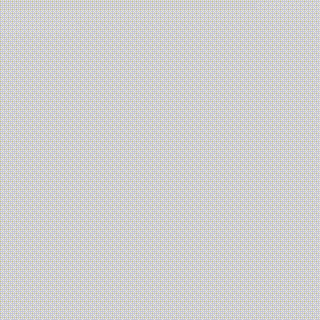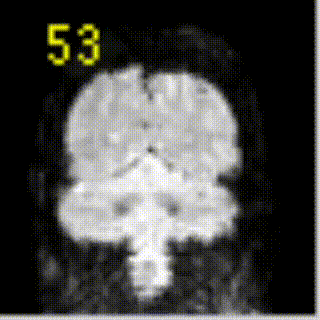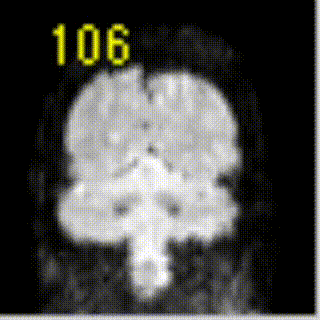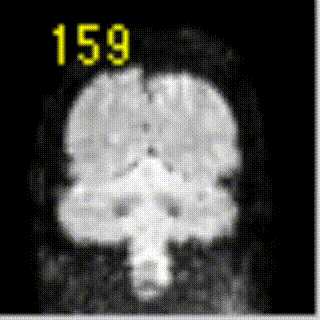
18 fMRI measures changes over time

19 “There is no free lunch”
- both, spatial resolution and temporal resolution, are limited
- often, experimenter has to trade off one against the other
- so, different choices for different applications…
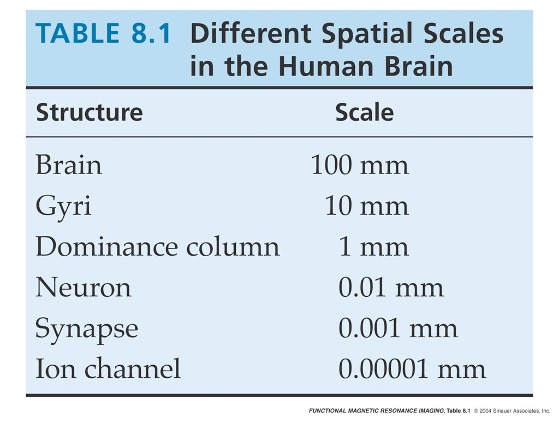
20 Why do we need high spatial resolution?
brain structures of interest are ~mm in size, sometimes separated by ~cm; need appropriate sampling
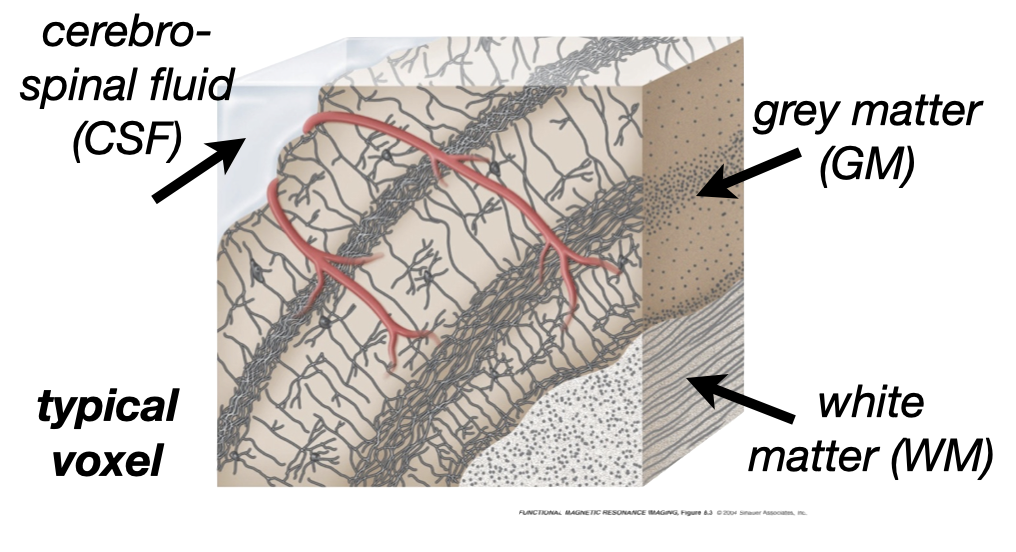
smaller voxels: less mixing of grey matter, white matter, CSF, veins, … reduced partial voluming
21 Appropriate sampling
22 Volume → no. of cells
… if packing density in grey matter of cortex is ~50,000 cells / mm\(^3\)
| edge (mm) | volume (mm\(^3\)) | #cells in pure GM |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 50k |
| 3 | 27 | 1.35M |
| 5 | 125 | 6.25M |
23 PVE
24 Partial volume effects
25 What limits (spatial) resolution
hardware (the scanner)
the subjects
- peripheral nerve stimulation PNS
- specific absorption rate SAR limits
- time in scanner ( >1.5h is not fun)
signal-to-noise ratio - smaller voxels = proportionally more noise head motion, physiology, …
26 fMRI measures changes over time

27 What limits (temporal) resolution
physiology
basis of the blood-oxygen-level-dependent (BOLD) signal
- BOLD is haemodynamic, an indirect measure of neural activity (+ still hotly debated)
- BOLD signal is delayed and blurred in space, but also in time
28 Haemodynamic response
the shape of the response to a brief event is called the haemodynamic response function (HRF)
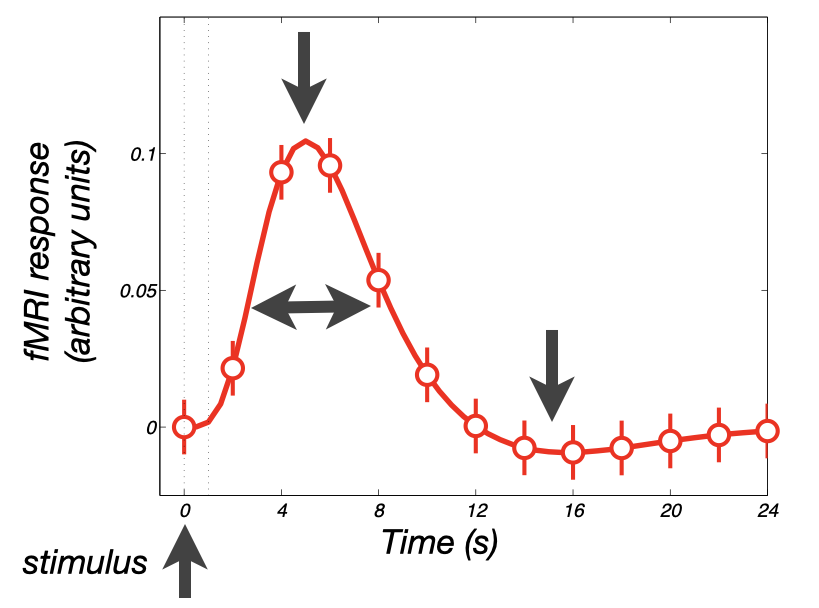
e.g. haemodynamic response to a 1s visual stimulus peaks several seconds later and is spread out
29 Intermediate summary
Overview of the fMRI method.
How to interpret fMRI data.
Limiting factors of fMRI.
Trade-off between temporal and spatial resolution.
Thinking about temporal resolution particularly important when designing fMRI experiments
30 Some principles of experimental design
Why do we need to worry about designing experiments?
31 Terminology
- Independent Variable:
-
variable which is intentionally manipulated (different manipulations are called conditions / levels)
- Dependent Variable:
-
measured variable
- Confound:
-
a property that co-varies with the IV
32 eg. this experiment
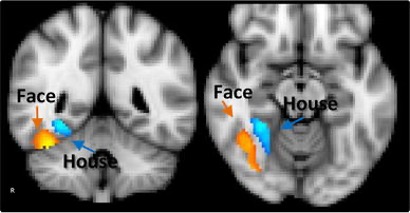


33 Dealing with confounds
Counterbalancing: a process for removing confounds by ensuring they have equal influence at each level of the IV
Randomization: removing confounds by making sure they vary randomly at each level of the IV
34 Within or between subjects?
Within-subjects designs are stronger as they control for:
- Age Gender.
- Experience.
- Individual Difference.
- Brain size / shape.
Between-subjects designs are sometime unavoidable
- Diagnostic comparisons
- Gender effects
Match the design to the research question…
35 … and for fMRI?
All the above, plus…
- Selecting an appropriate IV
- Selecting an appropriate control condition
- Types of experimental design
- Stimulus presentation timing
36 Many studies: cognitive subtraction
Compare two very similar conditions that are assumed to differ only in one property.

37 Control conditions are important

38 fMRI designs
Block Designs – trials appear in alternating blocks (Task A, Task B)
Event Related Designs – stimuli are presented one-at-a-time in a random order
Mixed Designs – alternating blocks of tasks but with mixed trials
(resting state fMRI) - no task
39 Block designs

Powerful for detecting signal changes if a good control is selected.
Not very good for estimating the shape of the HRF.
Sensitive to noise (scanner drift)
The block length is very important to consider
40 Event-related designs
come in two “flavours”
Slow – stimulus followed by long inter-trial intervals (eg 10-15s rest)
Fast/Rapid variable – rapid stimulus presentation with variable, but short ISI (2s)
41
42
43 Summary
Principles of experimental psychology apply to good fMRI study design also.
Consider how the hypotheses make predictions about space and time (and do they align with the scope of what fMRI can measure).
The experimental design should be appropriate for the research question.
Timing of stimulus presentation is key!
44 Thanks
See you soon!
45 Colophon
This presentation was made with
quartoandrevealjs.Uses a font called
Atkinson Hyerlegible, which was designed to work better for people with low vision: available via google fonts.
